Ind AS 10: It is impossible for any company to present the information on the same day, as the day of reporting. There would always be a gap between the end of the period for which financial statements are presented and the date on which the same will actually be made available to the public.
During this gap, there is a possibility of occurring of few events which will have far reaching effects on the business / existence of the company. Now the question arises: what view the company should take about such events? Should it leave it without any cognizance as they are taking place after the reporting period, or should it take cognizance of such events as at the time of making it public? If the company is aware of the facts and is still not disclosing the same, it may mislead the users.
List of other IndAS
Ind AS 10
Events after the Reporting Period: The objective of IndAS 10 is to prescribe:
- when an entity should adjust its financial statements for events after the reporting period; and
- the disclosures that an entity should give about the date when the financial statements were approved for issue and about events after the reporting
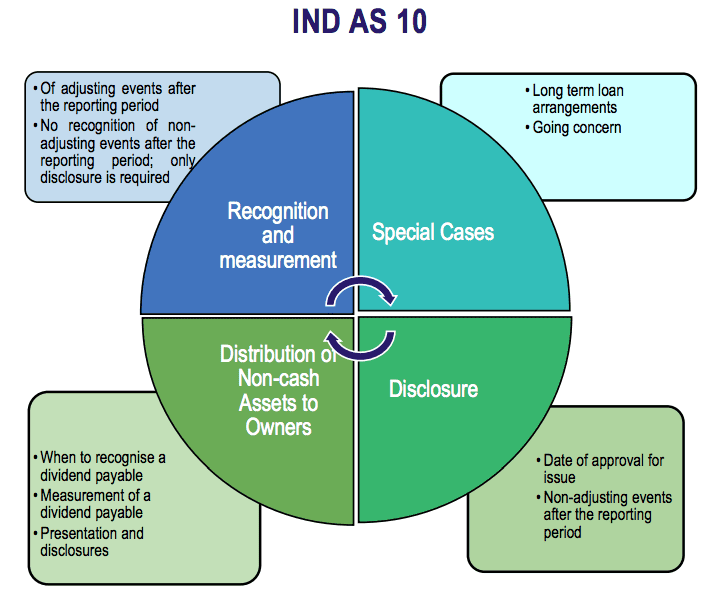
The Standard also requires that an entity should not prepare its financial statements on a going concern basis if events after the reporting period indicate that the going concern assumption is not appropriate.
Advertisement
Content in this Article
Events after the reporting period are those events, favourable and unfavourable, that occur between the end of the reporting period and the date when the financial statements are approved by the Board of Directors in case of a company, and, by the corresponding approving authority in case of any other entity for issue. Two types of events can be identified:
- those that provide evidence of conditions that existed at the end of the reporting period (adjusting events after the reporting period); and
- those that are indicative of conditions that arose after the reporting period (non-adjusting events after the reporting period).
However, there is an exception to the above principle. In case of a breach of a material provision of a long-term loan arrangement on or before the end of the reporting period with the effect that the liability becomes payable on demand on the reporting date, the agreement by lender before the approval of the financial statements for issue, to not demand payment as a consequence of the breach, shall be considered as an adjusting event.
An entity shall adjust the amounts recognised in its financial statements to reflect adjusting events after the reporting period.
An entity shall not adjust the amounts recognised in its financial statements to reflect non-adjusting events after the reporting period.
However, if non-adjusting events after the reporting period are material and their non-disclosure could influence the economic decisions that users make on the basis of the financial statements, then it shall disclose the following for each material category of non-adjusting event after the reporting period:
- the nature of the event; and
- an estimate of its financial effect, or a statement that such an estimate cannot be
If an entity receives information after the reporting period about conditions that existed at the end of the reporting period, it shall update disclosures that relate to those conditions, in the light of the new information.Appendix A of Ind AS 10 provides guidance with regard to distribution of non – cash assets as dividends to owners. The Appendix prescribes that liability to pay such a dividend should be recognised when it is appropriately authorised and is no longer at the discretion of the entity. This liability should be measured at the fair value of assets to be distributed. Any difference between the carrying amount of the assets distributed and the carrying amount of the dividend payable should be recognised in profit or loss when an entity settles the dividend payable.
Events after the Reporting Period
Events after the reporting period are those events, favourable and unfavourable, that occur between the end of the reporting period and the date when the financial statements are approved
Example The financial year of an entity ends on 31st March, 20X2. If the board of directors approves the financial statements on 15th May, 20X2, ‘after the reporting period’ will be the period between 31st March, 20X2 and 15th May, 20X2 and the events occurring during this period should be considered as ‘events after the reporting period’.
Ind AS 10 Vs AS 4
| AS 4 | Ind AS 10 |
| AS 4 requires the same to be disclosed in the report of approving authority. | Ind AS 10 requires the disclosure of material non-adjusting events in the financial statements. |
| AS 4 does not contain any such appendix. | Ind AS 10 includes an appendix titled “Distribution of Non-Cash Assets to Owners”, which is an integral part of Ind AS 10. Along with this, it also deals with when to recognize dividends payable to owners. |
| AS 4 only requires adjustment to assets and liabilities. It does not require a fundamental change in basis of accounting. Further, it also does not require any such disclosure, as is required by Ind AS 1. | If after the reporting date, it is determined that the going concern assumption is no longer appropriate, Ind AS 10 requires a fundamental change in the basis of accounting.
In this regards, Ind AS 10 refers to Ind AS 1, which requires an entity to make following disclosures:
|
| AS 4 is silent on this aspect. However, Guidance Note on Schedule III, issued by ICAI states that considering that the practical implications of the breach are negligible in the Indian scenario, the entity should continue to classify the loan as “Non Current” as on the Balance Sheet date, provided that the loan is not actually demanded by the bank at any time prior to the date on which the financial statements are approved. | The definition of “Events after reporting period” in Ind AS 10 contains a proviso, which specifies that:
|
Recommended Articles

