Key Features of GST Bill: The GST Council will soon roll out the fitment of goods into the rate slabs as well as the final rules relating to GST. State legislatures are also expected to enact to approve the SGST legislations in respective states. Jammu and Kashmir will have to pass special laws to introduce GST as the current Constitutional status does not mandate it.
Main Features
- Concurrent jurisdiction for levy and collection of GST by the Centre (CGST) and the States (SGST)
- Centre to levy and collect IGST on supplies in the course of inter-State supplies and on imports
- Compensation for loss of revenue to States for five years
- All transactions and processes only through electronic mode – Nonintrusive administration
- PAN Based Registration
- Registration only if turnover more than Rs. 20/40 lac (Rs. 20 lac for special category States except JandK)
- Option of Voluntary Registration § Composition threshold shall be Rs. 150 lac (1.5 Crore)
- Composition scheme shall not be available to inter-State suppliers, service providers (except restaurant service) and specified category of manufacturers
- Deemed Registration in three working days
- Input Tax Credit available on taxes paid on all procurements (except few specified items)
- Set of auto-populated Monthly returns and Annual Return
- Composition taxpayers to file Quarterly return
- Automatic generation of returns
- GST Practitioners for assisting filing of returns
- GSTN and GST Suvidha Providers (GSPs) to provide technology based assistance
- Tax can be deposited by internet banking, NEFT / RTGS, Debit / credit card and over the counter
- Concept of TDS for certain specified categories wef 01.10.2018
- Concept of TCS for E-Commerce Companies wef 01.10.2018
- The e-way bill system has been introduced nation-wide for all inter-State movement of goods with effect from 01.04.2018. As on 16.06.2018, all States and Union Territories have introduced e-way bill system for intra-state movement of goods
- Refund to be granted within 60 days
- Provisional release of 90% refund to exporters within 7 days
- Interest payable if refund not sanctioned in time
- Refund to be directly credited to bank accounts
- Comprehensive transitional provisions for smooth transition of existing tax payers to GST regime
- Special procedures for job work
- System of GST Compliance Rating
- Anti-Profiteering provision – National Anti-Profiteering Authority already set up
- Standing Committee on Anti-Profiteering already set up
- State level Screening Committee already set up
Key Features of GST Bill
- GST is a major milestone in indirect tax reforms in independent India. GST is a common and unified tax on goods and services. It is a destination based consumption tax. It is applicable all over India including Jammu and Kashmir. It adorns dual taxation model where Union and states levy and collect taxes simultaneously. It ensures seamless flow of input tax credit to a large extent. It has been designed to be fully automated and online. A giant portal called GSTN is being used to ensure working of the GST system which is the IT backbone of GST.
- Actual GST rates would however be a four-tier tax structure of 5, 12, 18 and 28 per cent as approved by the GST Council
- The first country to implement Goods and Services Tax was France in as early as 1954.
- India has the highest tax slab in the world i.e., 28%, next only to Argentina which is at 27%
- Almost 160 countries around the world follow this scheme of indirect taxation
- Indian GST has four rate structure, viz. 5%, 12%, 18% and 28% with cess on sin goods and luxury items
- There is a special rate of 3% on precious metals like gold
- GST is covered under five legislations i.e., Central GST Act, State GST Act, Integrated GST Act, Union Territory GST Act and GST (Compensation to States) Act
- Integrated GST, Compensation cess and Central GST are charged by Central Government
- All taxation policies and their implementation are based on the recommendations of the GST Council
- The taxable event under GST is supply
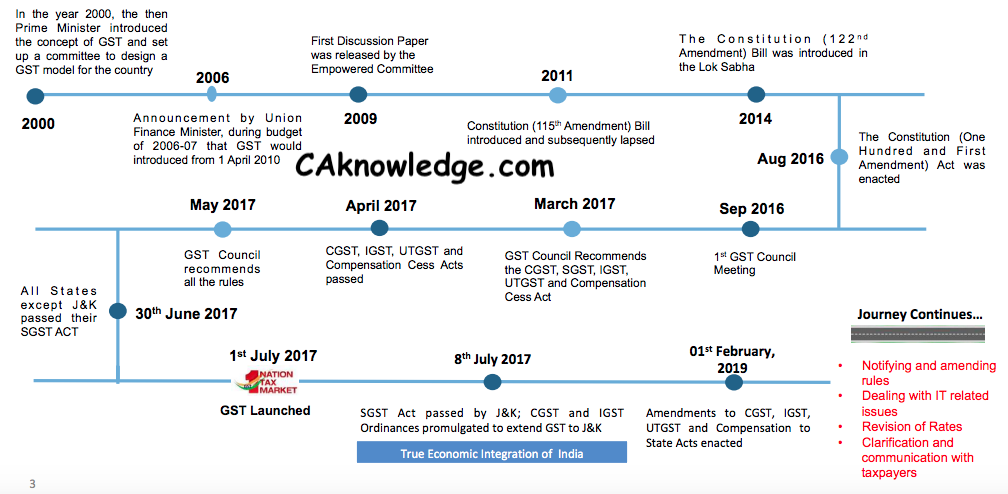
- GST Bill was introduced under 122nd Constitutional Amendment Bill, but passed under 101st Amendment Act, 2016
- Assam was the first state to ratify GST Bill but Telangana was the first state to pass State GST Bill
- GST Council was constituted with its headquarters in Delhi. The Union Finance Minister is the Chairperson
- State Finance Ministers are members of GST Council
- 1st July will be observed as the GST day
- The threshold limit under GST is Rs. 20 Lakhs, for some special category states it is Rs. 10 Lakhs
- There is a special purpose vehicle called GSTN which caters the IT needs of GST. GSTN comes under Companies Act, 2013 with combined stake of Central and State Governments is 49%. The rest is contributed by LIC Finance with 11% and ICICI Bank, HDFC, HDFC Bank and NSE Strategic Investment Corporation with 10% each.
- GST Council is meeting frequently to monitor and modify taxation policies. In order to simplify the procedures, it relaxed the system of filing the returns for small suppliers upto the annual turnover of Rs.1.5 crore. These suppliers can file returns quarterly instead of monthly.
- The GST Council also recommended a uniform policy on e way bill which is being implemented all over the country. This totally eliminates the check post system breaking the entry barriers and reducing bottlenecks in transportation.
- GST Council has also reviewed the rate structure of GST on goods and services. It also recommended reduction of rates on cases of merit.
Recommended Articles
- GST Registration
- GST Objective
- When will GST be applicable
- GST Forms
- GST Rate
- GST India
- GST Login
- GST Overview
If you have any suggestion regarding “GST Bill Key Features, Salient Features of GST Bill 2017” then please tell us via below comment box…

