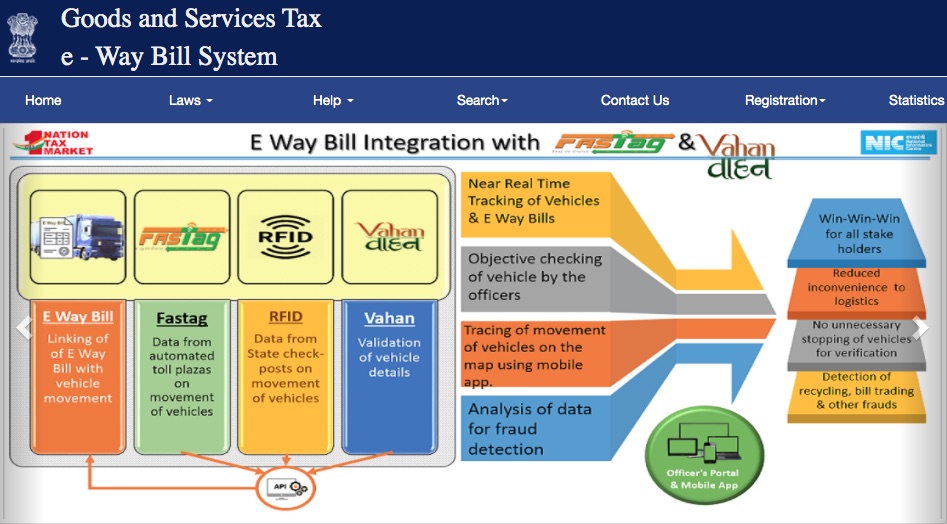
Basics of E-Way Bill: Since the roll out of the new regime from 1st July 2017 called Goods and Service tax Act, widely use as GST, the government is using the optimum utilisation of digital mode and electronic platform for major compliances, the initiative of go digital is managing the overall show of the tax compliance and E way bill is one of them, after the introduction of eway bill department is aggressively managing the movement of the goods through the digital platform and stake holders are also abiding the nation’s rules and regulations. E-invoicing and E-way bill both are pathbreaking initiative taken by the government.
Basics of E-Way Bill
According to rule 138 of the CGST rules, 2017 every registered person who makes movement of the goods and the value of the goods is exceeding Rs.50000 E-way bill is required to be generated and carried by a person in charge of the conveyance carrying the goods as required under the Goods and Services Tax Act.
E-way bill can be generated either by the Supplier or by recipient himself if the transportation is being done in own/ hired conveyance or by railways by air or by Vessel, in case If the consignment is given to a transporter for transportation by road, E-way bill is to be generated by the Transporter.
There may be situation where goods are sent by a principal located in one State to a job worker who is located in another State, in the given instance the e-way bill shall be generated by the principal irrespective of the value of the consignment.
E-way bill has two Components-Part A and Part B
- Part – A (Form GST EWB-01) comprising of details of
- GSTIN of recipient, Place of delivery (PIN Code),
- Invoice or Challan and date,
- Value of goods (Qty and rate), HSN code, transport document number (Goods receipt Number or Railway Receipt Number or Airway Bill Number or Bill of Lading Number and reasons for transportation; and
- Part B (GST EWB-01) comprising of transporter details (Vehicle number).
Advertisement
E-way bill is to be generated from the GST Common Portal for E-Way bill system (https://ewaybillgst.gov.in) by the registered persons (Supplier or recipient) or transporters who initiate the movement of goods but before the commencement of such movement, basically, it is a proof of physical movement of goods.
Further, it is necessary to upload all the information by the person who causes the movement of goods on the portal in order to generate E-Way Bill this information is to be uploaded prior to the commencement of movement of goods.
Upon generation of the e-way bill on the common portal, a unique e-way bill number (EBN) will be generated by the common portal, shall be made available to the supplier, the recipient and the transporter on the common portal.
Need of E-Way Bill
To grow with the vision of becoming super power economy it is important to place rules to curb the tax evasion and E-way bill initiative is one of its which ensure that goods being transported comply with the GST Law and is an effective tool to track movement of goods and check tax compliance.
Now let’s understand the practicality of E-way bill Validity of E-way bill
The validity of an E-way Bill or a consolidated E-way Bill depends on the distance for which the goods have to be transported.
- Upto 100 KM – One day
- Every 100km or part thereof – Additional one day from the relevant date
(Each day shall be counted as 24 hrs), In general, the validity of the e-way bill cannot be extended.
The “relevant date” here means the date on which the E-Way Bill is generated.
Additionally, there might be situations where goods cannot be transported within the specified validity period due to some unforeseen circumstances. In such cases, the transporter can generate another E-Way Bill after revising the information in Part B of Form GST EWB-01.
Cancellation of E-way Bill
In normal situation it is necessary to generate an Eway bill before the movement of goods, but there are circumstances where E-Way Bill is generated but due to some reason:
- goods are either not transported or
- are not transported according to the details specified in the E-Way Bill
In the given scenario the e-way bill may be cancelled electronically on the common portal, either directly or through a Facilitation Centre notified by the Commissioner within 24 hours of generation of the e-way bill. However, an e-way bill cannot be cancelled if it has been verified in transit in accordance with the provisions of rule 138B of the CGST Rules, 2017.
Non- compliance of provision – Consequences thereon:
As per rule 138 of the CGST Rules 2017, tax payer needs to generate E-way bill and if it is not generated, the same will be considered as contravention of rules and tax payer may face consequences for non-compliances. As per Section 122 of the CGST Act, 2017, a taxable person who transports any taxable goods without accompany of required documents (e-way bill) shall be liable to a penalty of Rs.10,000/- or tax sought to be evaded (wherever applicable) whichever is greater.
Furthermore, if any tax payer transports or stores goods in transit in a manner that is against the provisions of the Act. In such cases, following would be liable for detention or seizure:
- goods transferred
- vehicle (conveyance) used to transport such goods and
- documents relating to such goods and vehicle (conveyance)
Special cases – E way bill generation in Bill to and Ship to scenario:
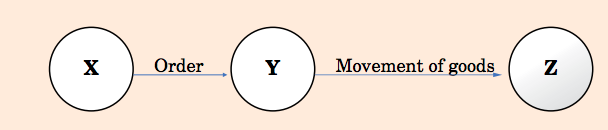
In ideal scenario there are 3 parties are involved in a bill to ship to transaction, viz, party 1 who order goods to party 2 and ask to deliver the goods to party 3, kindly have a look on below-mentioned illustration to understand it in better way.
- “X” is the party who has ordered “Y” to deliver the goods to “Z”.
- “Y” is the party who is sending goods directly to “Z” on account of “X”.
- “Z” is the ultimate recipient of goods.
In the above given illustration there are two supplies are involved and accordingly two tax invoices are needs to be prepared by concern parties:
- Tax Invoice -1 would be prepared by “Y” to “X”.
- Tax Invoice -2 would be prepared by “X” to “Z”.
Even It is clarified from the CGST Rules, 2017 either “X” or “Y” can generate the e-Way Bill, in the given situation only one e-Way Bill is required to be generated.
Blocking and unblocking of E-way bill:
Blocking:
From 02 December 2019 it empowers digital interface to block or unblock the generation of Eway bill in a specific situations. Like, If the taxpayer who has not filed 2 or more GSTR 3B returns consecutively over the GST portal the automated systems will block the tax payer in generating any new Eway bill.
Unblocking:
Once the default return period is less than 2 months the system automatically unblock the Eway bill generation and tax payer allows to use the utility of generation of Eway bill.
In certain situation e waybill Is Not required to Generate. There are situations where generation of Eway bill it is not mandatory and they are:
- In respect of movement of goods within such areas as are notified under rule 138(14) (d) of the SGST Rules, 2017 of the concerned State.
- If the distance is below 10km and the goods transported from seller’s place to the transporter’s place for further transportation.
- Goods being transported through non-motor vehicle.
- The goods transported from airport, air cargo complex and land customs station to an inland container depot or a container freight station. Provided goods are transported for clearance by customs.
- Cases with regards to specified goods such as diamond, jewellery, personal and household effects etc. These goods are prescribed in the list of items for which E-Way Bill is not needed.
- When Value of goods is below Rs. 50,000
Since the introduction of E-way bill systems, GST department has remarkably stopped the evasion of tax, in our opinion to make it more user and tax payer friendly the provision of penalty and in hand collection of tax can be reworked in the larger interest of stake holder.
Recommended Articles