Rent Control Act has been enacted and implemented by all the State Governments to protect the legitimate rights of the tenants. Primarily it focuses on controlling the rent and protection of protect tenants from unauthorized eviction by landlords. Following are the key issues dealt by rent control act:
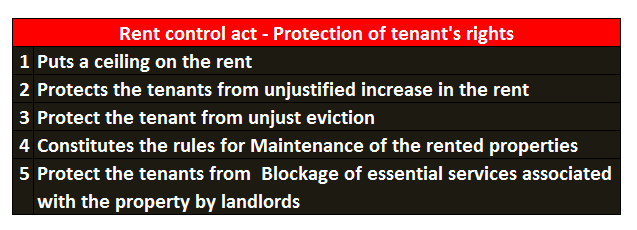
1. Rent control Act:
Rent control acts imposes a ceiling on the rental amounts that are charged by all types of housing facilities. Though the landlord of the premises is entitled to fix the rent, he should consider the prevailing market rates and the maximum ceiling as determined by the government. This ensures that no artificial surge is created by the landlords by creating a situation of scarcity of housing for rentals.
2. Permitted Increase in the rent:
Rent control acts of the majority of the states set the period for which if the rental agreement is made, the act does not allow any modification to be made in the rental amount be paid without the mutual consent of the both parties. Once the period is over and there is a mutual consensus on extending the agreement, the landlord can increase the rent by the percentage as provided in the rent control acts respective states. This restriction laid down by the rent control act would protect the tenants from unjustified increase in the rent of the property.
3. Protect the tenant from unjust eviction:
- As per the Rent Control Act, landlords can evict the tenants only under specific grounds such as willful default in rent payment, subletting without the prior consent etc.
- Most of the states have laid down strong provisions against the indiscriminate eviction of a tenant from the property.
- There is a Supreme Court judgment saying that a landlord cannot indiscriminately evict a tenant for a period of five years if the rent was paid by the tenant on time. However, the landlord can evict a tenant if he wants to use the premises for his own bona fide use.
- However, the landlord will not be entitled to apply for possession of the premises for his own bona fide use, if there is a contractual tenancy, which is granted for a specific period.
4. Maintenance of the rented properties:
- As per the rent control acts, it is the responsibility of the landlord to maintain the house in good and tenantable condition.
- If the landlord neglects the tenant’s request to get the repairs done, by serving a notice of fifteen days or the number of days as specified in respective state acts, the tenant can carry out repairs and deduct the cost incurred from the rent payable to the landlord. The only condition that comes forth here is that these repairs should not exceed by the ceiling limit (which is mostly certain portion of the annual rent) set by the respective acts.
- However, the act also provides for the landlord and the tenant to share the financial burden of the repair in the circumstances as constituted thereon.
5. Blockage of essential services associated with the property:
A landlord is not entitled to halt the essential services which are complimentary to the premises such as power and water or restrict a tenant from using common amenities for recovery of rental dues or for any other reasons. If a landlord stops any such services, the tenant can approach the court to restore essential services and take action against the landlord.
Recommended Articles
