History of GST worldwide, Historical Background of GST (Goods and Service Tax). Check Status of GST Law 2021, GST Journey so far. GST History in India, France is the first country in the world, which has implemented GST in 1954. In India Finance Ministry has placed 122nd Constitution Amendment Bill in Lok Sabha in 19th December, 2014. The Government of India has appointed various committees , task force to give their views to introduce a vibrant and modern Indirect Tax Structure in India, some of views are ;
The long-awaited GST regime is all set to roll out with the President assent to the following four GST related Bills :
- Central GST Bill, 2017
- The Integrated GST Bill, 2017
- Union Territory GST Bill, 2017
- GST (Compensation to States) Bill, 2017
The law will replace various indirect taxes with one simple tax, creating a boundary less and a unified national market that will also lead to increase in country’s GDP. Implementation of GST would bring many professionals opportunities for Company Secretaries in Practice and employment in terms of compliance, advisory, tax planning, etc
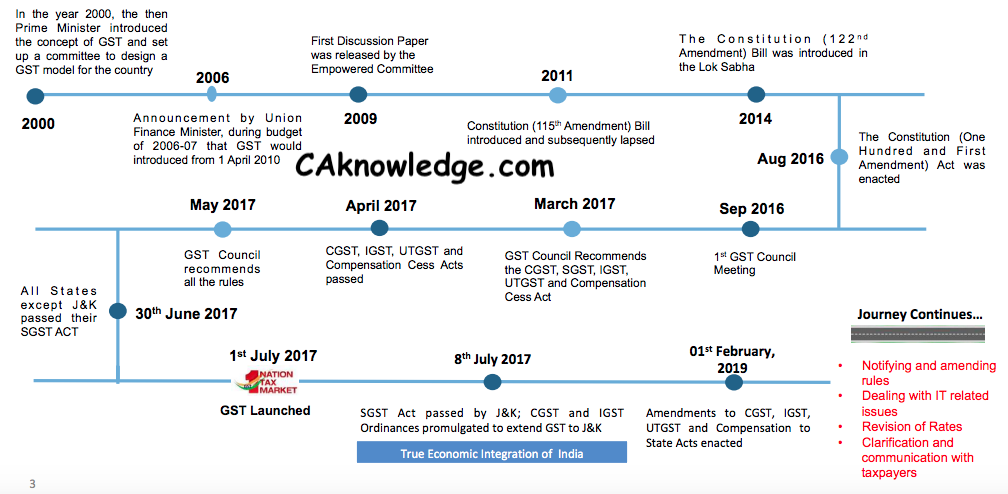
The comprehensive tax structure passed through various stages before being implemented
History of GST, Historical Background of GST
Advertisement
The origin of Goods and Services Tax could be traced back to July 17, 2000, when the Government of India set up the Empowered Committee of State Finance Ministers with the Hon’ble State Finance Ministers of West Bengal, Karnataka, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Punjab, Uttar Pradesh, Gujarat, Delhi and Meghalaya as members with the following objectives:
- to monitor the implementation of uniform floor rates of sales tax by States and Union Territories;
- to monitor the phasing out of the sales-tax based incentive schemes;
- to decide milestones and methods of States to switch over to VAT; and
- to monitor reforms in the Central Sales Tax system existing in the country.
History of GST
- Amaresh Baghchi Report, 1994 suggests that the introduction of “ Value Added Tax (VAT) ‘ will act as root for implementation of Goods and Services Tax in India
- Ashim Dasgupta, 2000 empowered committee, which introduces VAT System in 2005, which has replaced old age taxation system in India.
- Vijay Kelkar Task Force 2004, it strongly recommended that the integration of indirect taxes into the form of GST in India.
- Announcement of GST to be implemented by 1st April, 2010 after successfully implementation of VAT system in India and suggestion of various committees and task forces on GST, the Union Government first time in Union Budget 2006-07 announced that the GST would be applicable from 1st April, 2010.
- The government has formed various Joint Working Groups of state finance ministers to study the impact of GST on the revenue of various States.
- The empowered committees of State Finance Ministers after various meetings reached on amicable formula for implementation of GST in India.
- Task force of Finance Ministers has submitted their report in December, 2009 on structure of GST in India.
- Government of India has issued first discussion paper in November, 2009.
- Constitution (115th Amendment) Bill introduced on 22nd March, 2011 and same was referred to Parliamentary Standing Committee on Finance for discussion.
- March, 2011: The Constitution (One Hundred and Fifteenth Amendment) Bill, 2011 to give concurrent taxing powers to the Union and States was introduced in Lok Sabha. The Bill suggested the creation of Goods and Services Tax Council and a Goods and Services Tax Dispute Settlement Authority. The Bill was lapsed in 2014 and was replaced with the Constitution nd (122 Amendment) Bill, 2014.
- November, 2012: A “Committee on GST Design”, consisting of the officials of the Government of India, State Governments and Empowered Committee (EC) was constituted.
- March, 2013: A not for profit, non-Government, private limited company was incorporated in the name of Goods and Services Tax Network (GSTN) as special purpose vehicle setup by the Government primarily to provide IT infrastructure and services to the Central and State Government(s), tax payers and other stakeholders for implementation of the Goods and Services Tax (GST).
- August, 2013: The Parliamentary Standing Committee submitted its Report to the Lok Sabha. The recommendations of the Empowered Committee (EC) and the recommendations of the Parliamentary Standing Committee were examined by the Ministry in consultation with the Legislative Department. Most of the recommendations made by the Empowered Committee and the Parliamentary Standing Committee were accepted and the Draft Amendment Bill was suitably revised.
- Finance Minister in his speech announced that the GST will be rolled out by April, 2011.
- In August, 2013 Standing Committee on Finance tabled its Report on GST Bill
- In December, 2014 revised Constitution Amendment Bill was tabled in Parliament
- Constitution (122nd Amendment) Bill introduced in the Parliament in December, 2014; since 115th Amendment Bill has been lapsed due completion of parliamentary terms. The Government of India has introduced Constitution (122nd Amendment) Bill on 19th December, 2014 the Lok Sabha has passed the bill on 6th May, 2015 but Bill is pending in Rajya Sabha.
- On June 14, 2016, the Ministry of Finance released draft Model law on GST in public domain for views and suggestions.
- GST Bill Passed in Rajya Sabha on 3rd August 2016 (03-08-2016)On August 03, 2016, the Constitution (122nd Amendment) Bill, 2014 was passed by Rajya Sabha with certain amendments.
- The changes made by Rajya Sabha were unanimously passed by Lok Sabha.
- After the passage of the Amendment Bill in the Rajya Sabha and the changes subsequently ratified and passed by the Lok Sabha unanimously, the Bill was adopted by a majority of State Legislatures wherein approval by at least 50% of the State Assemblies was required.
- The final step to the Constitution (122nd) Amendment Bill, 2014 becoming an Act was taken when the Hon’ble President of India gave his final assent on September 8, 2016.
- The Constitutional 101st Amendment Act came into force which empowers both the States and Centre to levy this tax.
- In March 2017 –GST Council finalizing the GST Rules and GST Rates
- In April 2017 -Four GST related Bills become Act following Presidents assent and passage in Parliament:
- Central GST Bill
- Integrated GST Bill
- Union Territory GST Bill
- GST (Compensation to States) Bill
- In May 2017 -GST Council recommends all the rules
- 30th June 2017 -All States except JandK passed their SGST ACT
- 1st July 2017 -GST Launched
- 8th July 2017 –SGST Act passed by JandK; CGST and IGST Ordinances promulgated to extend GST to JandK
- 01st February, 2019 – Amendments to CGST, IGST, UTGST and Compensation to State Acts enacted
- Journey Continues…
GST Law from a Constitutional Perspective
Definition of GST -“Goods and services tax” means any tax on supply of goods, or services or both except taxes on the supply of the alcoholic liquor for human consumption
| Definition | Article | Definition |
| Goods | 366(12) | Includes all materials, commodities, and articles [Pre Existing Definition] |
| Service | 366 (26A) | Anything other than goods [Introduced vide 101st Constitutional Amendment Act] |
| State | 366(26B) | With reference to articles 246A, 268, 269,269A and Article 279A includes a Union territory with Legislature. [Introduced vide 101st Constitutional Amendment Act] |
“Goods and Services tax” law while having unique principles, has significant elements of prior Central and State laws; and is also inspired by VAT/GST legislation of EU, Australia, Malaysia etc. along with International VAT/GST guidelines of OECD
Bill passed by Rajya Sabha on 03.08.2016 and Lok Sabha on 08.08.2016
Notified as Constitution (101st Amendment ) Act, 2016 on 08.09.2016
Key Features:
- Concurrent jurisdiction for levy and collection of GST by the Centre and the States – Article 246A
- Centre to levy and collect IGST on supplies in the course of inter-State trade or commerce including imports – Article 269A
- Compensation for loss of revenue to States for five years on recommendation of GSTC – Clause 19
- GST on petroleum crude, high speed diesel, motor spirit (commonly known as petrol), natural gas and aviation turbine fuel to be levied from a later date on recommendations of GSTC
Status of GST Law 2017
The following laws have been passed by the Parliament followed by President’s assent :
| Law | Status |
| Central GST Bill, 2017 | Passed by Parliament followed by Hon’ble President’s assent |
| Integrated GST Bill 2017 | Passed by Parliament followed by Hon’ble President’s assent |
| Union Territory-GST Bill, 2017 | Passed by Parliament followed by Hon’ble President’s assent |
| GST (Compensation to States) | Passed by Parliament followed by Hon’ble President’s assent |
| State GST Bill, 2017 | To be passed in respective State Assemblies |
The 14th meeting of GST Council shall be held on 18-19 May, 2017 to finalize the fitment of commodities in the four- tier rate structure and to finalise draft rules. CBEC has issued total 11 GST rules as follows, which are available in the public domain on CBEC website :
- (i)GST Composition Rules
- (ii) GST Valuation Rules
- (iii) GST Transition Rules
- (iv) GST ITC Rules
- (v) GST Revised Invoice Rules
- (vi) GST Revised Payment Rules
- (vii) GST Revised Refund Rules
- (viii) GST Revised Registration Rules
- (ix) GST Revised Return Rules
- (x) GST Assessment and Audit Rules
- (xi) GST Electronic Way Bill Rules
Recommended Articles
- Key Definitions Under GST
- GST Overview With Example
- Tax Structure of GST
- When will GST be applicable
- Why GST For India
- GST Return
- GST Rates
- GST Registration
If you have any query or suggestion regarding “History of GST, Historical Background of GST” then please tell us via below comment box…

thank you . I ma very benifited by your information
thank you . I ma very benifited by your information
Its help me, to intoduce a seminar on my class, so thanks!
Its help me, to intoduce a seminar on my class, so thanks!
Its help me, to intoduce a seminar on my class, so thanks!