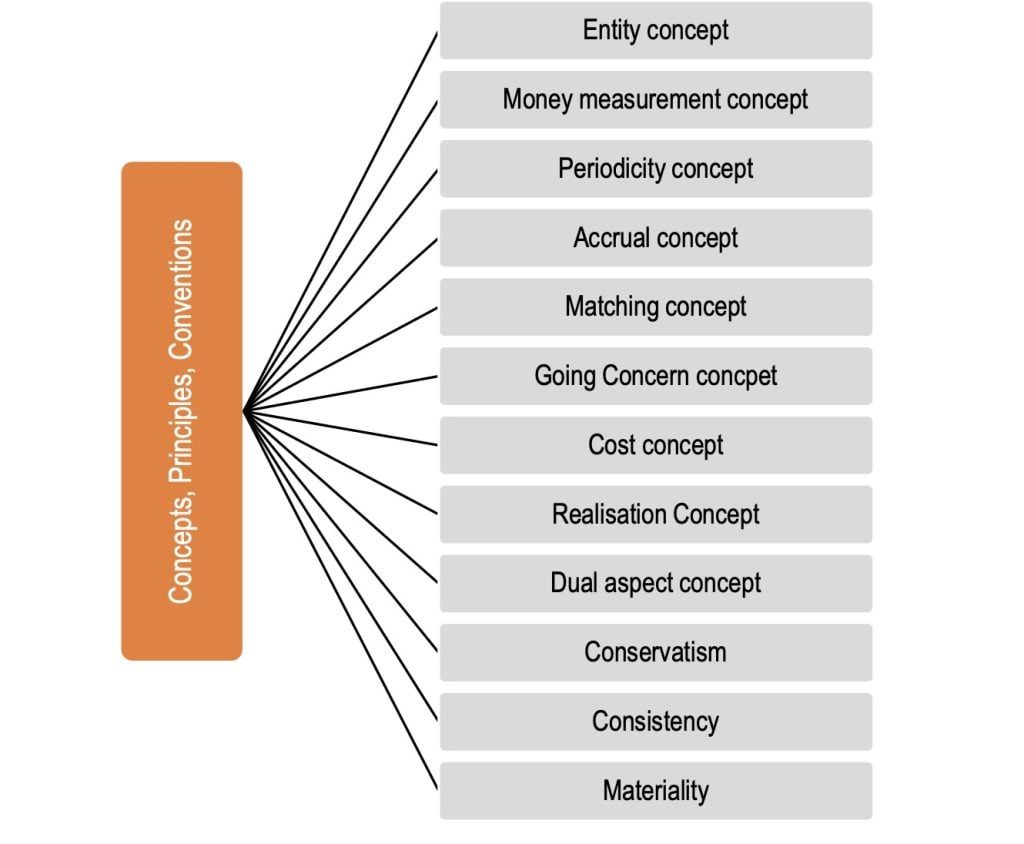
Basic Principles of Accounting and Golden Rules of Accounting. GAAP (Generally Accepted Accounting Principles) is the framework,andnbsp;rules and guidelines of the financial accounting profession with aandnbsp;purpose of standardizing the accounting concepts, principles andandnbsp;procedures. Top 10 Most Important Basic Accounting Principles Defined. Here is the list of top basic accounting principles that company follow quite often. Here are the basic accounting principles and concepts under thisandnbsp;framework :
Basic Principles of Accounting
1. Business Entity
A business is considered a separate entity from the owner(s) andandnbsp;should be treated separately. Any personal transactions of its ownerandnbsp;should not be recorded in the business accounting book, vice versa.andnbsp;Unless the owner’s personal transaction involves adding and/orandnbsp;withdrawing resources from the business.
2. Going Concern
It assumes that an entity will continue to operate indefinitely. In thisandnbsp;basis, assets are recorded based on their original cost and not onandnbsp;market value. Assets are assumed to be used for an indefinite period ofandnbsp;time and not intended to be sold immediately
3. Monetary Unit
The business financial transactions recorded and reported should beandnbsp;in monetary unit, such as INR,US Dollar, Canadian Dollar, Euro, etc.andnbsp;Thus, any non-financial or non-monetary information that cannot beandnbsp;measured in a monetary unit are not recorded in the accountingandnbsp;books, but instead, a memorandum will be used.
4. Historical Cost
Advertisement
All business resources acquired should be valued and recorded basedandnbsp;on the actual cash equivalent or original cost of acquisition, not theandnbsp;prevailing market value or future value. The exception to the rule is whenandnbsp;the business is in the process of closure and liquidation.
5. Matching Concept
This principle requires that revenue recorded, in a given accountingandnbsp;period, should have an equivalent expense recorded, in order to showandnbsp;the true profit of the business.
6. Accounting Period
This principle entails a business to complete theandnbsp;whole accounting process of a business over a specific operating timeandnbsp;period. It may be monthly, quarterly, or annually. For the annualandnbsp;accounting period, it may follow a Calendar or Fiscal Year.
7. Conservatism
This principle states that given two options in the valuationandnbsp;of business transactions, the amount recorded should be the lowerandnbsp;rather than the higher value.
8. Consistency
This principle ensures consistency in the accounting procedures usedandnbsp;by the business entity from one accounting period to the next. Itandnbsp;allows fair comparison of financial information between twoandnbsp;accounting periods.
9. Materiality
Ideally, business transactions that may affect the decision of a user ofandnbsp;financial information are considered important or material, thus, mustandnbsp;be reported properly. This principle allows errors or violations ofandnbsp;accounting valuation involving an immaterial and small amounts ofandnbsp;recorded business transactions.
10. Objectivity
This principle requires recorded business transactions should haveandnbsp;some form of impartial supporting evidence or documentation. Also, itandnbsp;entails that bookkeeping and financial recording should be performedandnbsp;with independence, that’s free of bias and prejudice.
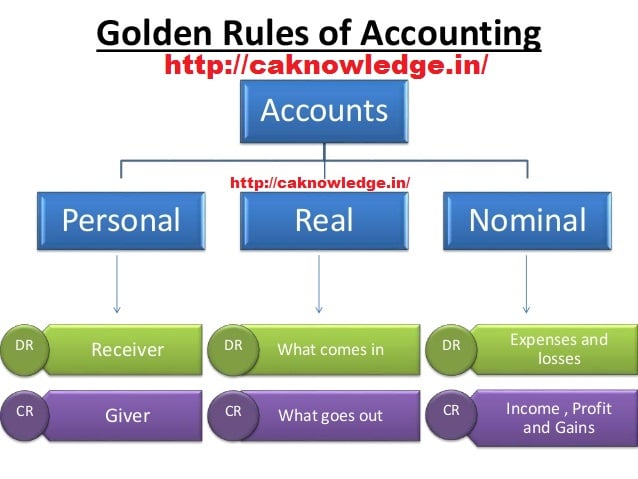
Golden Rules of Accounting :-
A] Real Accounts:-
1) Debit what comes in.
2) Credit what goes out.
B] Personal Accounts :-
1) Debit the reciver.
2) Credit the giver.
C] Nominal Accounts :-
1) Debit all expenses and Losses.
2)Credit all Incomes and Revenue.
Recommended Articles
Excellent
how can I download book of standard 12th.